 |
|

The knowledge representation paradigm MultiNet has shown its suitability for the semantic representation of natural language in many years of use at the University of Hagen. The core of the MultiNet representation is formed by semantic networks, which can be represented by directed graphs with nodes representing concepts from the discourse area and edges expressing relations between these concepts. Nodes and edges are enriched with various sets of attributes which establish a multi-layered structure of the network (each attribute partitions the nodes into classes or "layers" of nodes with the same attribute value). This multi-layered organization of the paradigm is reflected by the name MultiNet.
The work reported on this page was aimed at providing methods for representing knowledge in MultiNet, and at developing tools to support knowledge engineering tasks on the represented knowledge.
The programming library for building MultiNet applications was implemented in the Scheme programming language. It comprises the following functionality:
|
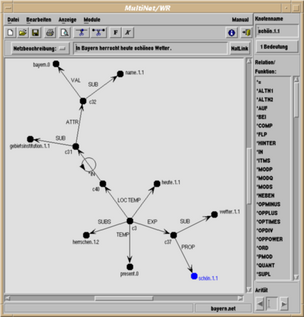
The knowledge engineering tool MWR (Multinet WissensRepräsentation, i.e. "MultiNet knowledge representation") was designed to aid the knowledge engineer in creating and editing MultiNet knowledge bases, and to simplify the development of applications in the MultiNet framework.
A graphical user interface permits the graphical display of MultiNet representations. Both the network and the layer attributes used to refine the concept descriptions can be edited in a WYSIWYG (What you see is what you get) manner. A large HTML-based help system assists the users by displaying information on selected MultiNet concepts. Automated consistency checks help prevent typical errors of users unacquainted with the MultiNet paradigm. The graphical user interface is complete with respect to the MultiNet ADT, so the knowledge engineer can view and edit all kinds of information stored in the knowledge base by using the graphical point-and-click interface.
MWR contains several tools for developing large and complex
semantic networks. An assimilation tool supports the user in merging
several small networks into a large knowledge base. This is a typical
task in creating a MultiNet representation from a large text body
translated to MultiNet in a sentence-by-sentence approach.
A layout component takes care of the geometrical arrangement of
automatically generated networks. Such networks are created by natural
language analysis or by an inference process).
MWR further supports external interfaces to the
WOCADI
parser for
word-class based analysis (WCFA) of NL inputs, and to the computer
lexicon
HaGenLex
(both
developed at this chair), which lets the users profit from these
components when building MultiNet knowledge bases.
Conversely, the MWR tool can also be accessed from the lexicon
workbench in order to edit knowledge related to lexical concepts
and to display the MultiNet analysis of example
sentences.
MWR is a development platform for MultiNet-based applications. The graphical network editor, the support for natural-language knowledge acquisition, the MultiNet ADT, and the inference component are all part of the MWR system. New MultiNet applications can be realized as plug-ins within the MWR system; by doing so, already existing services and tools within the MWR system become also available for the new application. For example, the MWR graphical user interface can be used to manually inspect results generated from the new application, and the editing facilities may be employed in the generation of special test cases for the new application.
See the guided tour of the MWR system for screenshots of the graphical user interface which illustrate the main components of MWR and its use as a platform for application development.
[Publications of the IICS Group]